What Is the 9-Box Grid Model?
If you need help assessing employee performance, you could draw a graph through which you can classify your employees based on two key factors: their current performance and potential for future growth. This is precisely what the 9-box grid allows you to do. By placing employees in one of the nine boxes, you classify them in a grading system that can inform decisions about training, development, and career progression.
In simpler terms, the 9-box grid helps you identify your top performers, those with high potential, and those who might need additional support and suffer from low performance. This allows you to strategically invest in your workforce and make sure you have the right people in the right roles, at present and in the future.
What Is the 9-Box Grid Model?
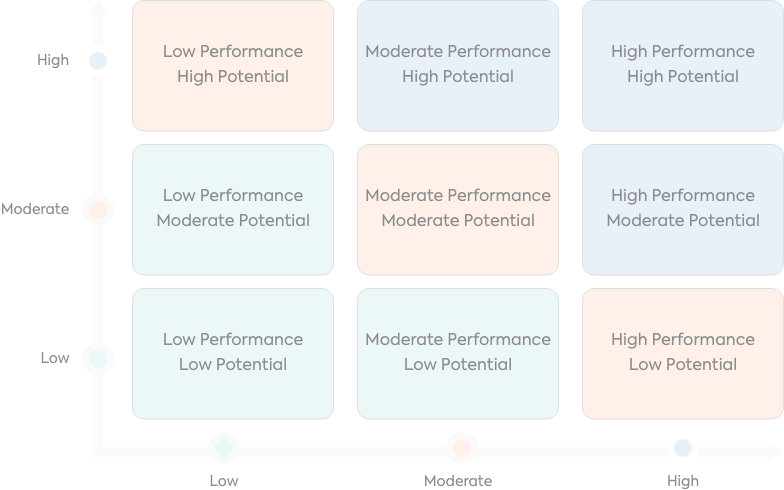
The 9-box grid model is a visual framework that categorizes employees into nine segments based on two key dimensions:
- Performance: This refers to an employee's current level of achievement and effectiveness in their role. It can be measured through performance reviews, key performance indicators (KPIs), or other objective data.
- Potential: This refers to an employee's ability and capacity for future growth and development. It's about what they can achieve beyond their current role. Assessing potential can involve considering factors like skills, experience, learning agility, and leadership qualities.
By plotting these two dimensions on a 3x3 grid, with employee performance on the X-axis and potential on the Y-axis, we set up the nine boxes. Each box represents a different category of employee, with specific talent management practices associated with it.
How to Use the 9-Box Grid
Now that we know what the 9-box model is, let’s take a further step and look at how to use it. Here, we’ll introduce a 5-step guide to creating a 9-box talent grid template and assessing your employees’ profiles.
Understanding the Axes
The performance (X-Axis) reflects how well an employee meets job performance expectations and achieves goals. Here's a breakdown of common categories:
- Poor Performance: The employee consistently falls short of expectations, doesn't meet targets, and may require significant improvement.
- Moderate Performance: The employee meets expectations and fulfills their role competently but may not necessarily exceed them.
- High Performance: The employee exceeds expectations, achieves ambitious goals, and demonstrates initiative.
The potential (Y-Axis) refers to an employee's ability and capacity for future growth and development. It's about what they could achieve, not just their current results. Look for these indicators:
- Low Potential: The employee may be at their full potential, have limited skills for growth, or lack the drive to progress.
- Moderate Potential: The employee can learn and develop further within their current role or move into slightly more senior positions.
- High Potential: The employee demonstrates a strong growth mindset, actively seeks to develop new skills, and exhibits the potential for significant future growth, possibly into leadership roles.
Step 1: Creating the Template
- Draw a 3x3 grid: Label the horizontal axis “Performance” (Low, Moderate, High) and the vertical axis “Potential” (Low, Moderate, High).
- Customize the boxes (optional): You can further define what each performance and potential level means for your organization. For example, “High Performer with High Potential” could be “A Star Employee” and “Low Performer with Low Potential” could be “The Wrong Hire.”
Step 2: Evaluating Performance
This requires a structured approach for each employee. Use the employee's job description and responsibilities to create a specific framework for their assessment. Consider factors like meeting targets, exceeding performance expectations, or consistently falling short.
Additionally, gather data from performance reviews, project evaluations, and feedback from managers and colleagues.
Step 3: Evaluating Potential
Potential is best measured by behavior and background. However, it’s trickier to assess, as it's not just about current results. Consider employees who are constantly developing their skills, who demonstrate a willingness to learn and apply new knowledge, who have good leadership skills, or a good educational background.
Here are some questions you can use during the evaluation:
- Learning and development: Do they actively seek learning opportunities, participate in training, and demonstrate a willingness to acquire new skills?
- Initiative and problem-solving: Do they take initiative, think creatively, solve problems independently, and come up with new ideas?
- Adaptability: Can they adjust to change, embrace new challenges, and perform well in a fast-moving environment?
- Leadership qualities: Do they demonstrate leadership potential by inspiring and motivating others, taking ownership, and building teamwork?
- Career aspirations: Does the employee express interest in moving up in the company and taking on more responsibility?
- Background: Has the employee performed successfully at previous jobs? What about the employee’s educational formation?
Step 4: Placing Employees on the Grid
Based on your assessments, determine where each employee fits on the grid. This should be a collaborative effort between managers, HR professionals, and leadership to build an accurate picture.
Encourage the exchange of ideas to gain a well-rounded overview of each employee's strengths and weaknesses and to avoid favoritism and biased perspectives. A company with a platform that allows employees to run safe, candid reviews will probably have higher-quality conversations—and maybe a more comprehensive outcome than what the grid offers.
Step 5: Taking Action
Now that you have a clear picture of your workforce through the 9-box performance grid, it's time to develop specific action plans for each category. Here's a simplified breakdown of action plans:
- High potential: Invest heavily in development for these future stars. This includes challenging projects, leadership training, mentorship, and career planning. Address any roadblocks to their success. Additionally, try to identify root causes for those high-potential employees who are not performing well. Are they under-stimulated in their current role? Do they lack specific skills needed to perform effectively? Are they unclear about expectations, disengaged, or facing personal challenges?
- Solid performers: For both moderate and high performers who are content in their roles, provide opportunities to maintain and improve their skills. This could involve ongoing training, enriched tasks within their area of expertise, or even mentoring junior colleagues. However, be careful not to over-reward low-potential but high or moderate performers, as they may lack ambition and the opportunity to move and grow despite their good work.
- Performance issues: For underperformers, regardless of potential, a clear performance improvement plan (PIP) is necessary. This may involve targeted training, coaching, or even alternative placements within the organization. In severe cases, outplacement services or termination might be considered.
Remember, the 9-box grid is a tool to guide development, not a rigid system. As obvious as it may sound, the key is to align the action plan to the individual's needs and the organization's goals.
Advantages of the 9-Box Grid Model
The 9-box grid can be a helpful tool for organizations seeking to optimize their performance management process. Its strength lies in its simplicity and ease of use. The clear visual structure makes it very easy to distinguish between employees based on their current performance and future potential, allowing even those new to the concept to grasp its impact.
But let’s go straight to the 9-box grid, which can be a useful tool for:
- Identifying talent: It can help identify employees with strong current performance and high potential for future growth. These individuals are valuable contributors and should be targeted for development opportunities.
- Workforce planning: The 8-box grid provides a snapshot of the skills and potential within your workforce. This information can be used to identify any skills gaps and plan for future needs.
- Succession planning: By identifying employees with leadership potential, the 8-box grid can help organizations develop a pipeline of future leaders.
Understanding the Limitations of the 9-Box Grid
While the 9-box grid offers simplicity and ease of use, it's very important to be aware of its drawbacks. These have some limitations to consider:
- Subjectivity: Assessments of both an employee’s performance and potential can be subjective, especially if they rely solely on traditional annual reviews.
- Oversimplification: The grid can paint an overly simplistic picture of complex employee capabilities. Potential is difficult to define and measure, and the grid can overlook valuable qualities that don't fit neatly into a box.
- Bias: Favoritism or personal opinions can influence where employees are placed on the grid.
- Labeling: Placing employees in a category can create a fixed mindset, keeping their growth.
- Transparency: Without clear communication about how the grid is used, it can lead to employee demotivation, especially for those in lower categories.
Alternative Approaches to the 9-Box Grid
The 9-box grid, while a familiar tool, has certain drawbacks. Here are some alternative approaches to consider for supplementing the grid or for a more comprehensive performance management strategy:
Performance Management Software
Modern HR software offers robust performance management tools that go beyond the static nature of the 9-box grid. Talent HR, for example, provides an employee performance management tool that includes features like:
- Continuous feedback: Regular check-ins and feedback loops allow for ongoing development and a more nuanced picture of performance.
- Centralized online reviews: Digital review systems simplify the process, reduce paperwork, and facilitate honest feedback through separate employee and manager forms.
- Data-driven insights: Software tracks performance data across the organization, enabling comparisons and identification of trends or potential issues. This data can then be used to inform future talent management strategies.
- Automated workflows: Automated review cycles maintain consistency and timely completion.
- Development and action planning: Performance reviews can be linked to career development opportunities, allowing for targeted skill development and growth.
360-Degree Feedback
Unlike the manager-centric approach of the 9-box grid, 360-degree feedback provides a holistic view by gathering input from a variety of sources. This can include self-assessment, supervisor feedback, peer feedback, and even feedback from subordinates or clients (depending on the role).
However, implementing a 360-degree program requires careful consideration of potential barriers, such as ensuring confidentiality, managing the time commitment involved, and dealing with the influence of personal bias in the feedback provided.
Skills-Based Assessments
Skills-based assessments offer a more objective approach by focusing on the specific skills and competencies required for the job. These assessments can take various forms, including technical skills tests, situational judgment tests, or work sample tests.
Challenges include the cost of developing or purchasing these assessments, the time commitment required for administration and evaluation, and the need to verify that the test results accurately reflect the specific job requirements.
9-Box Grid Related FAQs
Is the 9-box grid suitable for all organizations?
The 9-box grid can be a helpful starting point, but it might not be ideal for highly specialized roles or fast-paced environments where skills evolve quickly.
How often should we update the 9-box grid?
The ideal frequency depends on your industry and employee development pace. Consider monthly or semi-annual reviews, with adjustments as needed based on performance or skill development, for more accurate results.
Can the 9-box grid be integrated with other HR processes?
Yes, definitely. It can inform performance reviews, development plans, and even succession planning by helping identify high-potential employees.